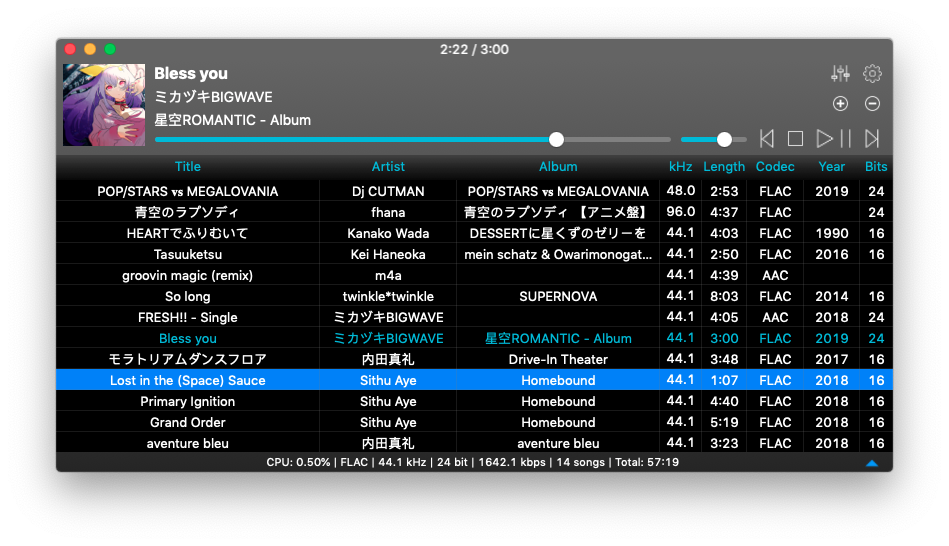
Fully utilizing a Mac’s potential, we have developed VOX's Audio Engine in our FLAC Music Player for Mac. In addition to common formats, including: FLAC, MP3, CUE, APE & M4A – you can also playback Hi-Res Audio (HD Audio) with up to 24bit/192kHz, at 4 times higher than the standard 44kHz sound resolution. For decades, Universal Audio has brought their legacy of creating top-quality audio gear to the modern generation of producers and engineers. Whether you're a pro or running a project studio, Sweetwater stands by Universal Audio's cutting-edge interfaces, revolutionary DSP, and classic analog music gear. Click to learn more about Universal Audio. There are three ways to get hi-res audio out of your Mac: 1) through an optical Toslink cable connected to the headphone output; 2) through a USB cable; and 3) through a standard stereo eighth. QuickTime Player, bundled with the Mac operating system, is Apple's flagship software. It ensures you to view Internet video, HD movie trailers, and personal media. This best media player for Mac is slick and easy to use. You can quickly export your videos to 4K, 1080P, 720P, 480P (based on original resolution) or extract them as M4A audio. Though it’s a video player, VLC supports FLAC audio files too. Forget about other players, this.
The following is an incomplete list of Linux audio software.
Audio players[edit]
GStreamer-based[edit]
Best Music Player Mac Os
- Amarok is a free music player for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. Multiple backends are supported (xine, helix and NMM).
- Banshee is a free audio player for Linux which uses the GStreamer multimedia platforms to play, encode, and decode Ogg Vorbis, MP3, and other formats. Banshee supports playing and importing audio CDs and playing and synchronizing music with iPods. Audioscrobbler API support.
- Clementine is a cross-platform, open-source, Qt based audio player, written in C++. It can play Internet radio streams; managing some media devices, playlists; supports visualizations, Audioscrobbler API. It was made as a spin-off of Amarok 1.4 and is a rougher version of said program.
- Exaile is a free software audio player for Unix-like operating systems that aims to be functionally similar to KDE’s Amarok. Unlike Amarok, Exaile is a Python program and uses the GTK+ toolkit.
- Guayadeque Music Player is a free and open-source audio player written in C++ using the wxWidgets toolkit.
- Muine is an audio player for the GNOME desktop environment. Muine is written in C# using Mono and Gtk#. The default backend is GStreamer framework but Muine can also use xine libraries.
- Quod Libet is a GTK+ based audio player, written in Python, using GStreamer or Xine as back ends. Its distinguishing features are a rigorous approach to tagging (making it especially popular with classical music fans) and a flexible approach to music library management. It supports regular expression and Boolean algebra-based searches, and is stated to perform efficiently with music libraries of tens of thousands of tracks.
- Rhythmbox is an audio player inspired by Apple iTunes.
- Songbird is a cross-platform, open-source media player and web browser. It is built using code from the Firefox web browser. The graphical user interface (GUI) is very similar to Apple iTunes, and it can sync with Apple iPods. Like Firefox, Songbird is extensible via downloadable add-ons. It's able to display lyrics retrieved from the net, and also the ones embedded through metadata (ID3v2 tag) after adding the LyricMaster plug-in. Linux official support for Songbird was discontinued in April, 2010. But in December, 2011 a group of programmers forked it openly as Nightingale.
Music Player Daemon based[edit]
- Cantata is a Qt-based front-end for Music Player Daemon.
- Ario is a light GTK2 client to MPD
Other[edit]
- aTunes is a free, cross-platform audio player for operating systems supporting the programming language Java (Unix-like: Linux, BSD, Macintosh), and Windows. aTunes can also play Internet radio streams and automatically display associated artist information, song videos, and song lyrics.
- Audacious is a free media player for Linux or Linux-based systems. It can be expanded via plug-ins, including support for all popular codecs. On most systems a useful set of plug-ins is installed by default, supporting MP3, Ogg Vorbis and FLAC files.[1] Audacious' classic interface looks and feels very similar to Winamp. It is compatible with LADSPA plug-ins.
- cmus is a small and fast text-mode music player for Linux and many other Unix-like operating systems.
- DeaDBeeF (as in 0xDEADBEEF) is a modular audio player for GNU/Linux, *BSD, OpenSolaris, macOS, and other UNIX-like systems.
- JuK is a free software audio player for KDE, the default player since KDE 3.2. JuK supports collections of MP3, Ogg Vorbis, and FLAC audio files.
- mpg123 is a real time MPEG 1.0/2.0/2.5 audio player/decoder for layers 1, 2 and 3 (MPEG 1.0 layer 3 a.k.a. MP3 most commonly tested). Among others working with Linux, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, SunOS4.1.3, Solaris 2.5, HPUX 9.x, SGI Irix and Cygwin or plain Windows. It is free software licensed under LGPL 2.1
- Music on Console (MOC) is an ncurses-based console audio player. It is designed to be powerful and easy to use, and its command structure and window layouts are similar to the Midnight Commander console file manager. It is very configurable, with Advanced Linux Sound Architecture (ALSA), Open Sound System (OSS) or JACK Audio Connection Kit (JACK) outputs, customizable color schemes, interface layouts, key bindings, and tag parsing.
- Sound eXchange (SoX) is a cross-platform command-line audio editor.
- X MultiMedia System (XMMS) is a GTK1-based multimedia player which works on many platforms, but has some features which only work under Linux. XMMS can play media files such as .ogg, MP3, MOD's, WAV and others with the use of input plug-ins. It is a free software audio player similar to Winamp that runs on many Unix-like operating systems. However, development of XMMS has been deprecated in favor of XMMS2, a new audio player built from scratch on the more modern GTK2 libraries. See also Audacious on this page as a successor to the historic XMMS.
- Tomahawk is a cross-platform music player built with social media and multi-source music streaming in mind. It features support for services like Spotify, Grooveshark, Dilandau, SoundCloud, 4shared, Jamendo, Last.fm, Ampache, Owncloud, Ex.fm and Subsonic.
Distributions and add-ons[edit]

- Planet CCRMA, an add-on for Red Hat Linux with many tools and system mods
- puredyne (Ubuntu based)
- Ubuntu Studio, an Ubuntu-based distribution geared toward multimedia
- AVLinux (Debian-based)
Graphical programming[edit]
- Pure Data (Pd), graphical programming language.
Audio programming languages (text-based)[edit]
- ChucK, an audio programming language for realtime synthesis, composition, and performance.
- Csound, composition, synthesis and processing.
- Nyquist, Lisp-based language for sound generation and analysis. Audacity supports plug-ins written in Nyquist.
- SuperCollider, a language like Smalltalk for real-time audio synthesis.
DJ tools[edit]
- Mixxx is a cross-platform and DJ package supporting a wide range of file formats, MIDI/HID controllers and timecode vinyl.
Drum machines[edit]
- Hydrogen, drum machine and sequencer
Recording, editing and mastering[edit]
Digital audio workstations (DAWs)[edit]
- Ardour, a multi-track audio recorder. GPLv2+
- LMMS, music composer. GPL
- Qtractor, a full featured multitrack digital audio workstation (DAW), with audio and MIDI sequencer. GPL
- REAPER, a proprietary multitrack audio, MIDI recording and mastering software.
- Rosegarden, MIDI sequencer. GPL
- Tracktion, proprietary and commercial digital audio workstation.
- Traverso DAW, a multi-track audio recorder. GPL
- Harrison Mixbus and Mixbus32C, proprietary.
- Bitwig Studio, proprietary and commercial digital audio workstation.
Audio editors and recorders[edit]
- Audacity, audio editor and recorder.
- Ecasound, audio recorder.
- Jokosher, audio editor.
- Sound eXchange (SoX).
- Sweep, audio editor.
Sequencers[edit]
- MusE, MIDI-audio sequencer.
- Renoise, commercial modern tracker-style sequencer.
- Rosegarden, a music composition and editing environment based on a MIDI sequencer.[2]
- Seq24, a loop based midi sequencer.
- MilkyTracker, an old-school tracker.
Other[edit]
- Baudline, signal analyzer.
- Buzztrax, music composer.
- Gnome Wave Cleaner, denoise, dehiss and amplify.
- Impro-Visor, edit and playback jazz solos over chord changes and rhythm.
- LinuxSampler, sampler.
- Mp3gain, adjust MP3 playback volume without re-encoding.
Sound servers[edit]
- aRts, the KDE 3 soundserver.
- Phonon, the multimedia framework provided by Qt 4 and used in KDE 4.
- Enlightened Sound Daemon (EsounD, ESD).
- JACK Audio Connection Kit (JACK), real-time sound server.
- Network Audio System (NAS).
- Network-Integrated Multimedia Middleware (NMM).
- PulseAudio, a sound server, drop-in replacement for EsounD.
- PipeWire, a server for multimedia routing and pipeline processing.
Synthesizers[edit]
- DIN Is Noise (din), software synthesiser, musical instrument, uses computer mouse as bow.
- FluidSynth, with the interface QSynth.
- Gnaural, binaural beat and pink noise synthesizer.
- LMMS, tracker, sequencer, synthesizer.
- Pianoteq, digital physical modeling of pianos and related instruments.
- PySynth, a simple software synthesizer in Python.
- TiMidity, Play-convert MIDI files as-to PCM
- Yoshimi, software synthesizer.
- ZynAddSubFX, software synthesizer.
Effects processing[edit]
- PulseEffects, effects processing for input and output audio streams with PulseAudio.
- FreqTweak, real-time audio processing with spectral displays.
- Linux Audio Developers Simple Plug-in API (LADSPA).
- Disposable Soft Synth Interface (DSSI), a virtual instrument (software synthesizer) plug-in architecture.
- Sound eXchange (SoX), the audio Swiss Army knife.
- LV2, is the new audio Linux standard for plug-ins.
Format transcoding[edit]
- Sound eXchange (SoX)
Radio broadcasting[edit]
- Airtime, an automation system for radio stations.
- Campcaster (discontinued), an automation system for radio stations.
- Icecast, free server software for streaming multimedia.
- OpenBroadcaster, LPFM IPTV broadcast automation tools.
Radio listening[edit]
- Streamtuner, browse and listen to hundreds of streamed radio stations.
Best Audio Player Mac
Score and tablature edition software[edit]
- Frescobaldi, score writer
- Denemo, score editor
- LilyPond, score typesetter
- NoteEdit, score writer
- MuseScore, score writer
- TuxGuitar, a tabulature editor, score writer and player oriented for guitarists.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'Audacious home page'.
- ^Rosegarden is a music composition and editing environment based around a MIDI sequencer that features a rich understanding of music notation and includes basic support for digital audio.
| Stable release | 6.0 (September 24, 2018; 2 years ago) [±] |
|---|---|
| Operating system | macOS, Mac OS 8, 9 |
| Type | Digital DVD player |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | https://support.apple.com/guide/dvd-player/welcome/mac |
| Part of a series on |
| macOS |
|---|
From version 10.0 to version 10.15: From version 11.0: |
|
DVD Player (formerly Apple DVD Player) is the default DVD player in macOS. It supports all the standard DVD features such as multiple audio, video & subtitle tracks as well as Dolby Digital 5.1 passthrough, DVD access URLs and closed captions. In some instances, users can choose which VOB file to open. DVD Player is also fully compatible with DVDs authored by DVD Studio Pro and iDVD, including HD DVDs by DVD Studio Pro.[1]
As of macOS Mojave, it has been updated to 64-bit, sports a new icon and has better Touch Bar support.
Limitations[edit]
DVD Player complies with most copyright laws, and will thus enforce most restrictive measures of DVD technology, such as region-restrictive encodings and user-inhibited operations ('disabled actions'). It does this even when using an all-region DVD drive. It will even force Apple's Grab (screen-grabbing) program to cease functioning through the Finder interface until the DVD Player application is quit, effectively preventing the user from taking screen captures of visual DVD content.
The software does not contain a DTS decoder, so DTS tracks cannot be played through the Mac's built in speakers or analog output. However, DTS tracks can be output to devices that have their own decoder, so playback is supported through outputs such as S/PDIF, DisplayPort and HDMI. It has never supported the ability to play Blu-Ray discs.[2]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^DVD Player 4.6 release notes
- ^Alderman, Nathan. 'Best apps for playing Blu-rays on your Mac in 2020'. iMore. Retrieved June 27, 2020.
